Venezuelan Economic and Social Performance Under Hugo Chávez, in Graphs |
| Written by Jake Johnston and Sara Kozameh |
| Thursday, 07 March 2013 17:26 |
1. Growth (Average Annual Percent) 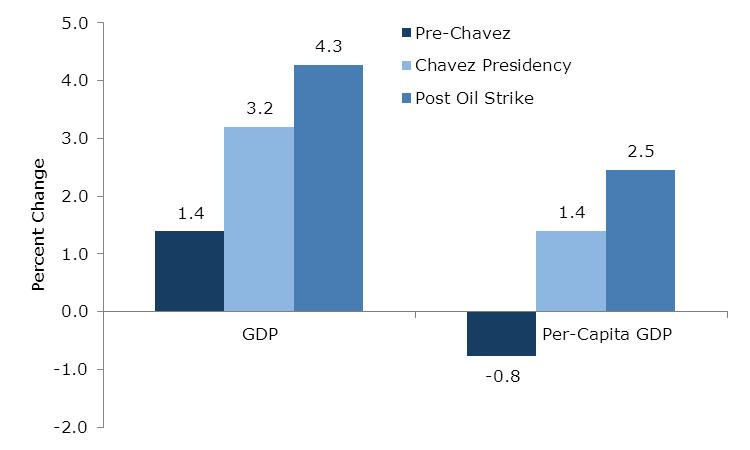 Source: Banco Central de Venezuela This graph shows overall GDP growth as well as per-capita growth in the pre-Chávez (1986-1999) era and the Chávez presidency. From 1999-2003, the government did not control the state oil company; in fact, it was controlled by his opponents, who used it to try to overthrow the government, including the devastating oil strike of 2002--2003. For that reason, a better measure of economic growth under the Chávez government would start after it got control over the state oil company, and therefore the economy. Above you can see this growth both measured from 2004, and for the 1999-2012 period. We use 2004 because to start with 2003, a depressed year due to the oil strike, would exaggerate GDP growth during this period; by 2004, the economy had caught up with its pre-strike level of output. Growth after the government got control of the state oil company was much faster. 2. Public vs. Private Growth – 1999-2012 (Average Annual Percent) 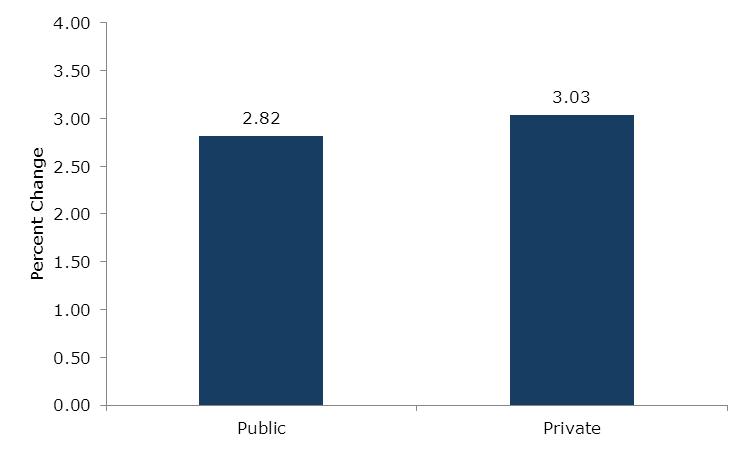 Source: Banco Central de Venezuela Source: Banco Central de VenezuelaThis graph shows the growth of the private sector versus the public sector during the Chávez years. 3. Inflation: Pre-Chávez vs. Chávez Years 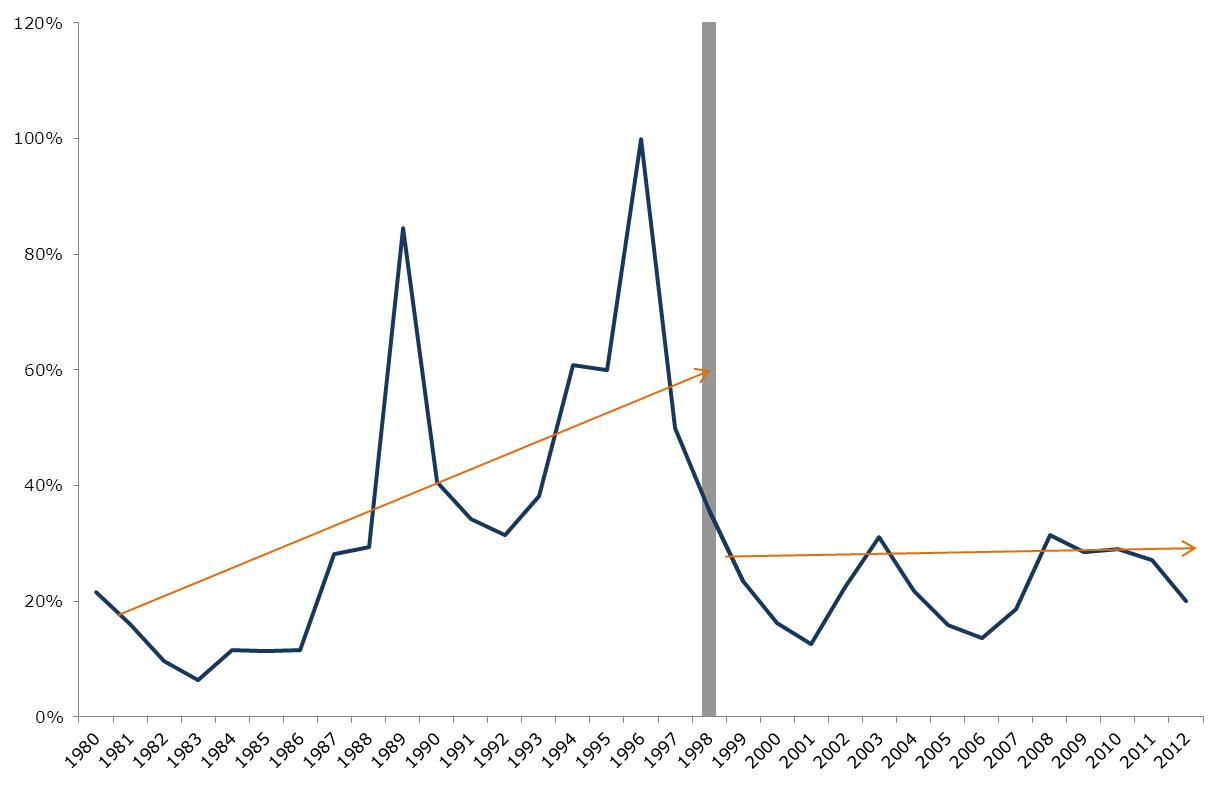 Source: Banco Central de Venezuela Source: Banco Central de VenezuelaInflation in Venezuela, consumer price index. 4. Unemployment Rate: Before and After Oil Strike 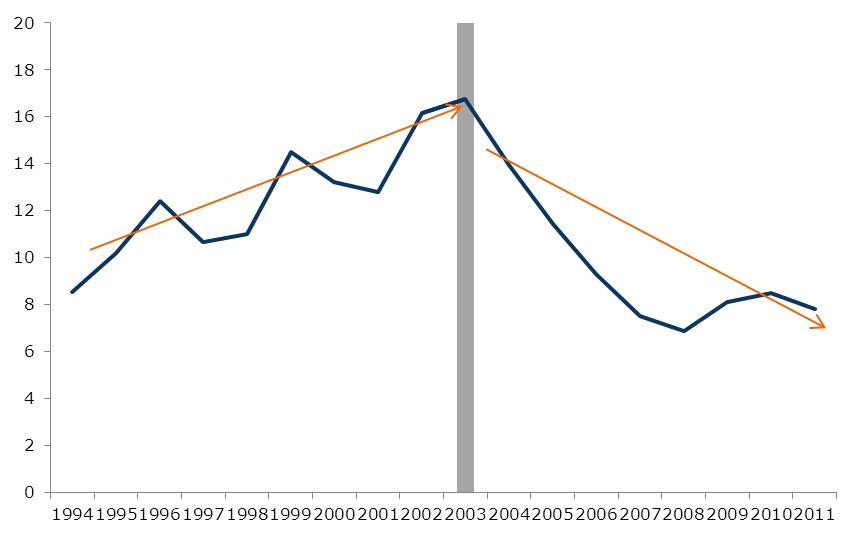 Source: Banco Central de Venezuela, INEC Source: Banco Central de Venezuela, INECAfter the oil strike (and the deep recession that it caused) ended in 2003, unemployment dropped drastically, following many years of increases before Chávez was elected. In 1999, when Chávez took office, unemployment was 14.5 percent; for 2011 it was 7.8 percent. 5. Poverty and Extreme Poverty Rate  Source: INEC Source: INECPoverty has decreased significantly, dropping by nearly 50 percent since the oil strike, with extreme poverty dropping by over 70 percent. 6. Gini Coefficient, 2001-2003 - Latin America  Source: Economic Commission on Latin America and the Caribbean Source: Economic Commission on Latin America and the CaribbeanThe Gini coefficient, measuring income inequality, fell from 0.5 to 0.397, the lowest Gini coefficient in the region. 7. Social Spending as a Percent of GDP  Source: SISOV Source: SISOVSocial spending doubled from 11.3 percent of GDP in 1998 to 22.8 percent of GDP in 2011. 8. Education: Net Enrollment  Source: SISOV Source: SISOV9. Graduates from Higher Education  Source: Ministerio del P.P. para la Educación Universitaria Source: Ministerio del P.P. para la Educación Universitaria10. Child Malnutrition- Age 5 and Under 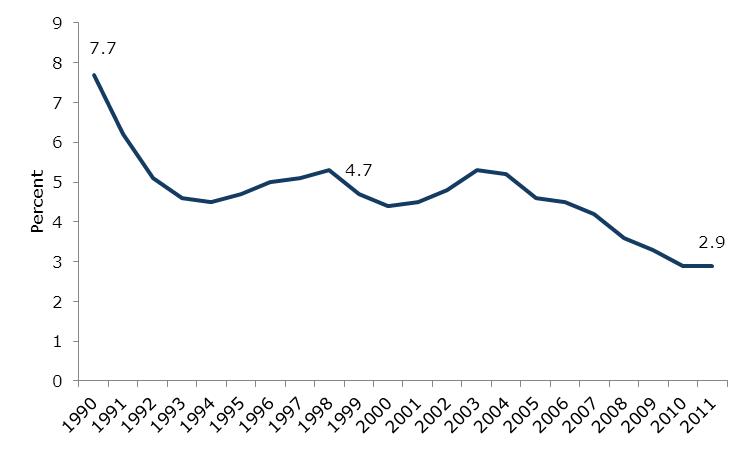 Source: Instituto Nacional de Nutrición Source: Instituto Nacional de Nutrición11. Venezuelans Receiving Pensions 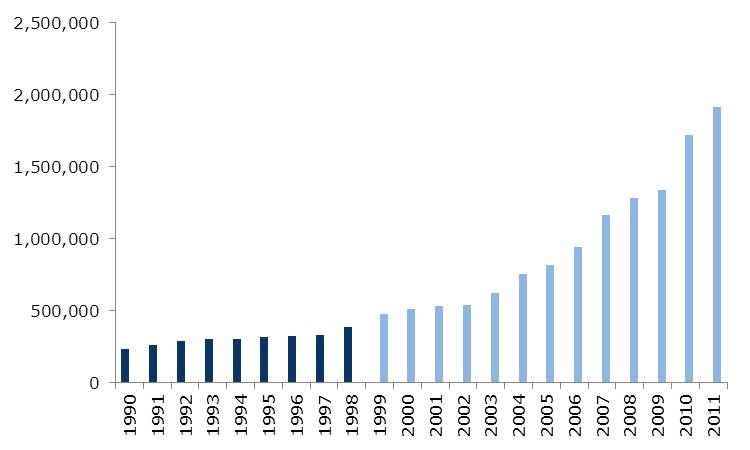 Source: Instituto Venezuela de los Seguros Sociales Source: Instituto Venezuela de los Seguros Sociales |